Risk factors of ocular melanoma
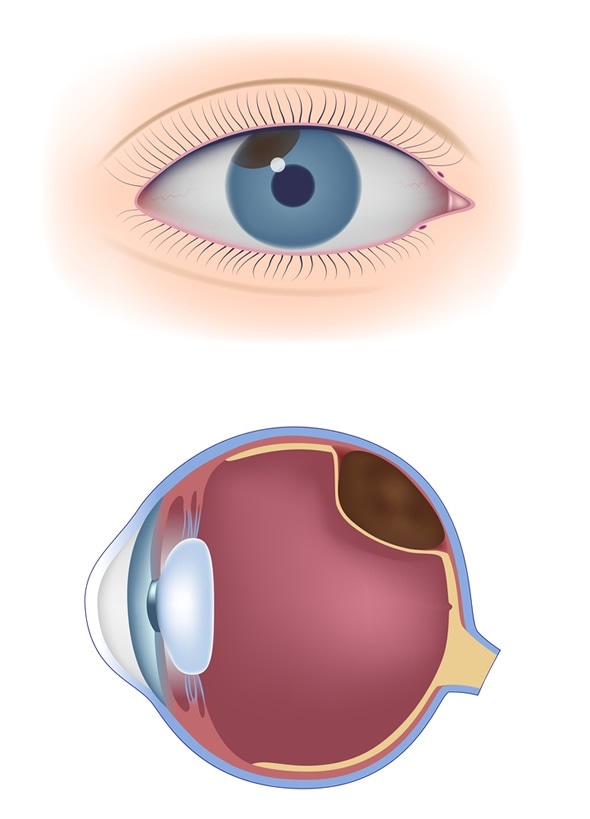
The most well-known type of eye malignant growth is melanoma (additionally called ocular melanomas) that regularly begins in the uvea or the centre a layer of the eyeball. The uvea is isolated into three sections: the iris (the shaded piece of the eye), the choroid (a dainty pigmented layer that lines the eyeball), and the ciliary body (contains the muscles inside the eye).
Ordinarily, eye melanomas create in the ciliary body or the choroid.
- ·
Auxiliary
eye malignant growths are tumours that have begun somewhere else and spread to
the eye and are more normal than the disease that starts in the eye. The most
well-known kinds of disease that can spread to the eye are bosom and cellular
breakdown in the lungs.
- ·
Age.
The normal age for a finding of eye malignancy is 55. Finding of eye malignancy
is uncommon in youngsters and grown-ups more established than 70 years old.
- ·
Eye
tone. Individuals with light shaded eyes are at a higher danger than those with
dull hued eyes.
- ·
Family
ancestry. Eye malignant growth can run in families, however, it is generally
uncommon.
- ·
Acquired
conditions, for example, dysplastic nevus disorder a condition that causes
irregular moles on the skin.
- ·
Race.
Caucasians will, in general, be more in danger for eye malignancy than
Hispanics or African Americans.
An excessive amount of openness to
daylight or UV rays, while a realized danger factor for skin malignancy, may
likewise, be a potential danger factor for eye disease, however, more
exploration is should have been sure.
On the off chance that your primary care the physician here in the oldest eye clinic in Brazil presumes eye malignancy, he may arrange imaging tests or an
ultrasound of the eye to help with a conclusion. Your PCP may likewise arrange
a chest X-ray or different tests to check whether the malignancy has spread to
different pieces of the body.
- · Seeing blazes of light or floaters in the eye
- ·
Loss
of sight in a part of your ocular field of sight
- ·
Different
issues with vision including obscured vision or unexpected loss of vision
- ·
A
developing a dull spot on the shaded piece of the eye
- ·
An
adjustment in the shape or size of the understudy
- ·
An
adjustment in the manner the eyeball is situated in the attachment
- ·
Swelling
of the eye
Those determined to have an essential eye
malignant growth, where the disease starts in the eye and has not spread, have
a high endurance rate. Therapy choices for eye malignancy may incorporate
straightforward perception to check whether the tumour develops, a medical
procedure to eliminate the tumour, radiation treatment, chemotherapy or
prescriptions.


Comments
Post a Comment